Just what is a microcontroller?
To get you understand quickly I define a micro controller as a single chip computer.Yes it is a full blown computer in its own. It has a C.P.U., RAM,some amount of EEPROM(for secondary storage i.e. permanent storage without power), many on-chip peripherals(Timer,Serial communication, Analogue to Digital converters etc.).If you don't understand, no problem I will be dealing them in detail in next tutorials. But compared to a P.C. their resources(RAM,speed etc)are less.But that is what is required !!! Because P.C. is a general purpose computer, which means it can run thousands of different softwares that are available for specific needs.Like it can run a game.The same P.C. can run this browser in which you are reading this!It can run a custom solution for banks,railways and airways.It can run a 3D modeling,video editing & image editing software for a production company. Many of these are huge software,requiring lots of memory and CPU power.And a P.C. can run simultaneously many of this !!! So to run them the host computer should have enough RAM and CPU power so that it can run heaviest of them. But in case of a microcontroller(aka MCU) which is used for a specific purpose like switching a Microwave oven heating off after a preset time,and also when temperature exceed preset value. |
A Typical MCU based solution. |
| |
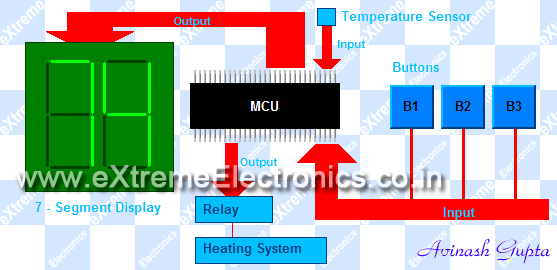 |
Block diagram |
| |
- Pen drives(for controlling the communication between P.C. and Flash Chip and also the small LED!)
- Hard disks( again for the same purpose)
- Mouse(Reads and Interprets the Sensors and send final result to P.C.),Keyboards
- Printers : Ever opened a printer for installing ink cartridge ? Then you must have seen the printed head. There are motors to control the print headl and the paper movement. Your P.C. is not directly connected to them but their is built in MCU of printer control all these. Your P.C. just sends the data(pixels) through the communication line(USB or parallel).But the MCU used here is fairly fast and has lots of RAM.
- Automobiles
- Calculators,Electronic wending machines, Electronic weighing scales, Phones(digital with LCD and phonebook)
- Cell phones
- Any thing that is small, but has great functions and is cheap !!!
A Simple MCU based system.
A simplest MCU system may look like below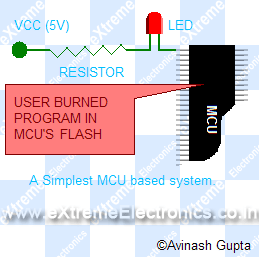 |
The program it is executing is like this( In C language).The MCU contains a flash memory where it stores its program(its like a hard disk to it). The flash memory can be easily erased and a new program can burned. This makes them very flexible. MCUs can be programmed few thousand times before they die. |
A Simple MCU Based System |
A Sample Program |
|
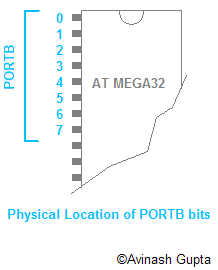 |
For example the image shows the PORTB and it bit numbering. Setting PORTB=0b00000001 will set PORTB's zeroth bit high that is 5V while remaining PINs will be low(GND).[NOTE:To write a binary number in c prefix it with 0b ex 0b00001000. It is decimal 8 not 1000 !!! ]The program above is not complete program it is just a pseudo-code.So it won't compile.Also you may be wondering where it will be entered, compiled and how the heck it will pushed into that chip?They are the subject of next tutorials and I will be covering them in detail. |
MCU Ports |
What the program does
STEP 1 SetPortDirection(); This Function Makes the PORTB as OUTPUT.Its implementation detail is not shown.
STEP 2 PORTB=0b00000001; makes the 0th bit high, switching off the L.E.D. because other end of LED is connected to VCC(i.e. Supply voltage 5V)
STEP 3 Delay(0.5); Halts the MCU for 0.5 Sec
STEP 4 PORTB=0b00000000; Switches on the LED
STEP 5 Delay(0.5); STEP 2 to 5 are within an infinite while loop so it runs till MCU is powered. The program is compiled, and burned into the chip and power is turned on and woillaaaa that LED is blinking once every second.You have just understood the "HELLO WORLD" program for MCU empire .Although the given program doesn't do something very important and can be done without a MCU and in a cheap manner, but it introduce you to microcontroller programming.Doing this with MCU has some advantages also.You can change the way LED blinks by simply writing a new program without touching the hardware part.You can also connect 8 LEDs to all 8 PINs of the PORTB, write a nice program them to light them in various pattern and you have a deluxe decorating lights !!! Which you can't make easily without MCUs.So you have seen that major functioning of a MCU project are made in software and hardware part is simple and small. So you have learned the basics of MCUs and their use.Hope you have nice time reading.So, good bye for now, we will meet in next tutorial.